Overview
The application enables visual comparative analysis of complete genome assemblies at different levels of resolution, using pairwise and multiple large-scale alignments. A visual representation of the alignments is comprised of two parts: graphs panel and alignments table, which are described in detail below.
Browser Compatibility
Vista Point supports all major web browsers including:
- Internet Explorer 6+
- FireFox 1.5+ (PC, Mac)
- Safari 3+
- Opera 9+ (PC, Mac)
Genome Selection
Analysis begins with the selection of a base genome and a compared genome from the pull-down menus shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1
Navigation
Use the controls located on the Chromosome Panel (Figure 2).
Figure 2
The navigation buttons along with the chromosome slider allow for zooming and panning
along the interval of the base chromosome.
The slider region represents the entire base chromosome/scaffold, while the "thumb"
(the greenish area) represents the region currently displayed in the panel above.
The displayed region can be specified explicitly by entering it into the position box and clicking Go.
Alternatively, you can enter a part of a gene symbol or name, in which case you will be prompted to choose from the list of genes,
that contain this pattern as part of their symbols or names.
The displayed region can also be changed by sliding or resizing the thumb (grabbing and dragging its edge).
The history support is leveraged by the location bar history of a web browser, allowing you to go back to the previous view, or forward to the next view in history, as well as to jump back or forward over the several views (Figure 3).
Figure 3
Graphs panel
Annotation. The gene annotation track is shown above the conservation curves, where dark and light blue boxes represent exons and UTRs respectively. Gene name appears underneath the track, the arrow points in the direction of the gene. (Figure 4).
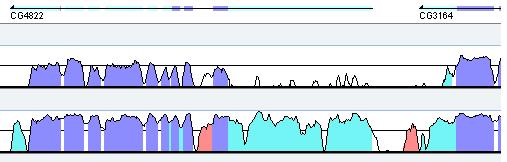
Figure 4
Some genomes may have multiple annotations available, in this case you can can display different annotations by selecting them from the "annotation" list box (Figure 5).
Figure 5
Peaks and valleys. The VISTA curve is calculated as a windowed-average identity score for the alignment. Each "peaks and valleys" graph represents percent conservation between aligned sequences at a given coordinate on the base genome according to the following:
Colored conserved regions. Regions are classified as "conserved" by analyzing scores for each base pair in the genomic interval, that is "Minimum Conserved Width" (default value 100 bp) and "Conservation Identity" (default value 70%). A region is considered conserved if the conservation over this region is greater than or equal to the "Conservation Identity" and has the minimum length of "Minimum Conserved Width". Regions of high conservation are colored according to the annotation as exons (dark blue), UTRs (light blue) or non-coding (pink). The thresholds that determine what gets colored, as well as minimum and maximum percentage bounds can be adjusted as the following:
Changing curve parameters. To adjust the parameters for a particular curve, click the "Vista Curve Parameters" button, a form with the adjustable parameters will appear (Figure 6).

Figure 6
Calc Window: The size of the sliding window used to calculate the conservation scores of each base pair used in the calculation of VISTA curve. Default is 100 base pairs.
Min Cons Width: Minimum width a conserved region must be before it is painted as such. Default value is 100 base pairs.
Cons Identity: Minumum percent conservation identity that must be maintained over the window ("Min Cons Width") for a region to be considered conserved. Default value is 70%.
Minimum Y: Lower boundary of the graph. Dropping the minimum Y value in areas of low conservation will allow you to see the smaller peaks. Default value is 50%.
Changing the order of curves. To change the order in which the curves are displayed on the panel, position the mouse cursor over the curve title (the cursor will be changed as an indication that the dragging is enable), and drag the curve to the new position.
Zooming.
To zoom in, click one of the "zoom in" buttons (+1.5x, +3x, +10x),
located on the Chromosom Panel,
or highlight the area of the graph you want to see in detail
by holding down the left mouse
button while moving the mouse over the region of interest,
just like you would highlight a sentence in Word. The browser will zoom in
on the selected area once you let go of the mouse button.
Alignments table
The table is located inside a resizable, collapsible panel, a panel's header contains a link to download a selected gene annotation of a base genome, and a link to a list of all conserved regions found (Figure 7).
Figure 7
The table lists each alignment that was generated for the base organism. Each row is a separate alignment. Each column, except the Tools, refers to the genome sequence that participate in a run. The Tools column contains information pertaining to the whole alignment (Figure 8).
Figure 8
The first cell of each row also contains a preview of the Vista plot of this particular alignment, which allows one to quickly evaluate the quality of this alignment and to see alignment overlaps.
Tools column provides links to alignments in human readable and MFA (multi-fasta alignment) formats, a list of conserved regions from this alignment alone (CNS), and links to PDF plots of this alignment alone. If the region being examined is 20K or less, rVista analysis can be performed, and a link to rVista will also be displayed here. This column also provides links to results of rankVista analyisis of the alignment. Read more about RankVista here.
By looking at a row in this table, you can see which section of each organism aligned to which. The Sequence links will return a fasta-formatted piece of the organism sequence that participates in the alignment. Clicking on the Vista Browser links will launch the applet with the corresponding organism selected as base, and the coordinates set to the coordinate of the selected alignment. Detailed help and instructions on the applet are available here.
The PDF file stores the visual representation of the alignment and found conserved regions, conservation and annotation coloring rules are similar to the graph panel described above. Gaps in the base sequence are signified by red sections of line underneath the plot. The color legend is summarized in the upper left-hand corner of the display. The gray lines under the plot show contigs, which are numbered in the case of draft sequences.